The ongoing coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks. As part of the global response to control it, both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical interventions have been instituted by several countries. However, one of the universal strategies being adopted is the use of face masks, this is to limit the transmission of the virus. Given the evidence of pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission of COVID-19, the use of face masks by apparently healthy persons especially in public places is highly recommended.
In line with the above, the Federal Government of Nigeria has mandated the mandated the use of face masks in public places. Asides the ongoing community transmission in all 36 States and the Federal Capital Territory in Nigeria, this step has become necessary given the gradual re-opening of most facets of our socio-economic activities.
Globally, in some settings, the spikes in the number of COVID-19 cases have been largely attributed to non-compliance with basic preventive measures such as wearing of face masks in public and observance of physical distancing measures. Emerging knowledge has also revealed that the use of face masks in wearing is most effective at limiting the spread of COVID-19 when compliance is high and when used appropriately especially in combination with other preventive measures.
To ensure widespread availability, affordability and compliance, the use of cloth face masks have generally been recommended as an alternative to medical masks. If made, worn, and maintained properly, they are effective and act as an additional protective layer of protection against COVID-19. The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has an advisory on the use of cloth face masks to provide guidance to the public on when, how and where to use face masks.
Therefore, to protect yourself and loved ones from COVID-19, face masks should be used in combination with the following protective measures:
1. Frequent handwashing with soap under running water or use of alcohol-based sanitiser where water is not available
3. Maintaining physical distancing of at least 2 metres between yourself and others
5. Adhering to other preventive measures as recommended by the Federal Government of Nigeria
We urge the public to continue to take responsibility by actively supporting efforts of the Nigerian Government to halt the spread of COVID-19. The NCDC will continue to provide necessary guidelines, protocols and advisories in line with the global best practices.
Summary of Incidents
Notes
1. Information for this disease was retrieved from the Technical Working Group and Situation Reports
2. Case Fatality Rate (CFR) for this disease is reported for confirmed cases only
3. Information for this disease was retrieved from IDSR 002 data
4. CFR for this disease is reported for total cases i.e. suspected + confirmed
5. Information for sentinel influenza was retrieved from the laboratory
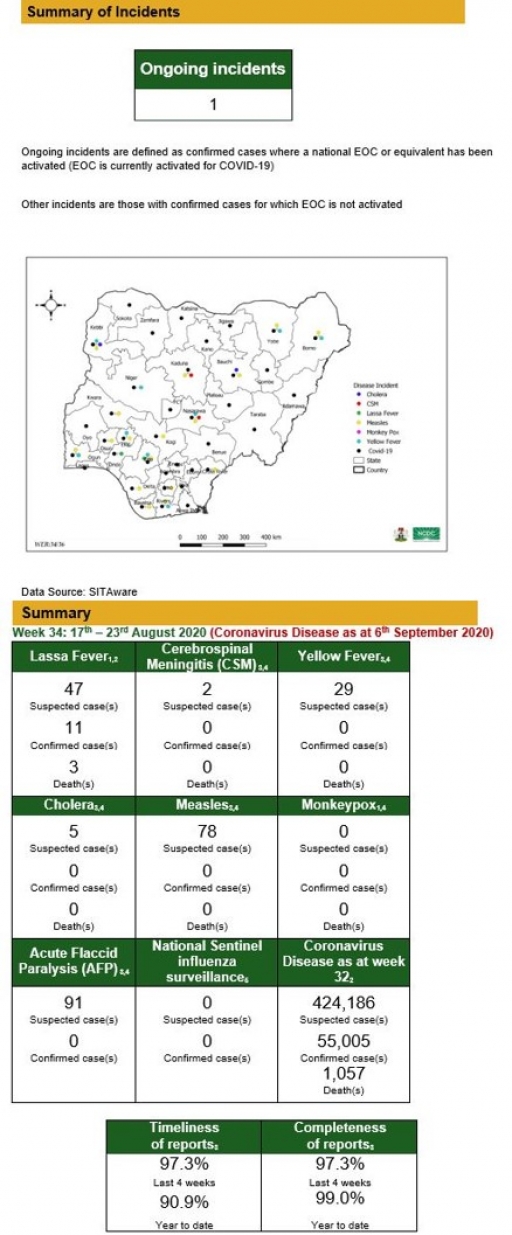
Lassa Fever
Key points
• There were 47 suspected cases, 11 were laboratory confirmed and three deaths were recorded from 20 LGAs in ten states.
• Two new healthcare workers were infected in Ondo state in the reporting week
Actions
To date:
• National Lassa fever multi-partner, multi-sectoral Technical Working Group (TWG) continues to coordinate the response activities at all levels
• Enhanced surveillance (contact tracing and active case finding) ongoing in affected states
Planned:
• Continue mobilisation of resources
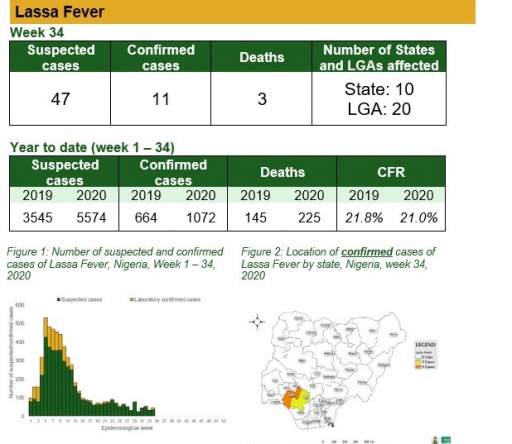
Cerebrospinal Meningitis (CSM)
Key points
There were two suspected cases of Cerebrospinal Meningitis (CSM) reported from two LGAs in two states (Kaduna – 1 & Nasarawa – 1). There was no laboratory confirmed case and no death was recorded
Actions
To date:
• National CSM TWG meets weekly to review reports from states and plan appropriately
• Enhanced surveillance in all states
Planned:
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
• Continue to ensure that states reporting cases send their line lists and collect CSM samples
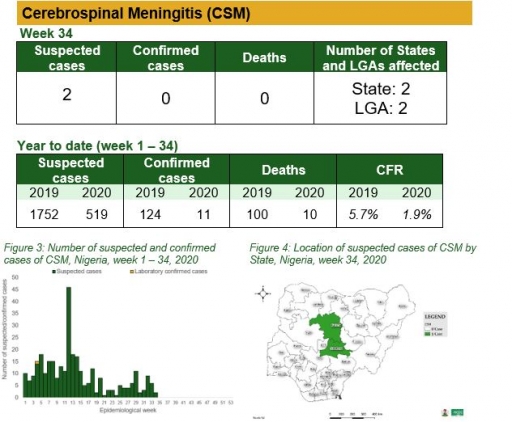
Yellow Fever
Key points
• There were 29 suspected cases of Yellow Fever (YF) reported from 21 LGAs in nine states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date:
• National multiagency YF Technical Working Group (TWG) is coordinating response activities
Planned:
• Continue harmonisation of surveillance and laboratory data ongoing
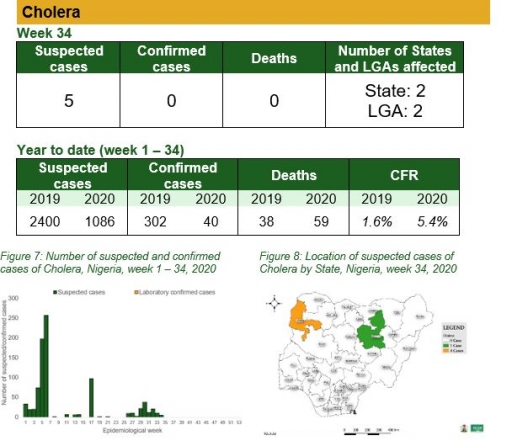
Cholera
Key points
• There were five suspected cases of cholera reported from two LGAs in two states (Bauchi – 1 & Kebbi – 4). None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date
• National Cholera Multi-Sectoral Technical Working Group (TWG) is monitoring all states and supporting affected states
Planned:
• Continue follow up and monitoring of non-reporting states
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
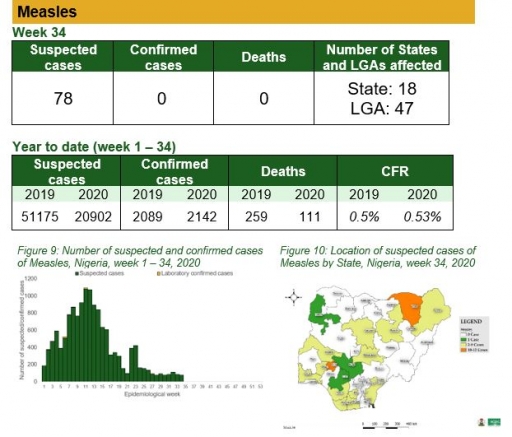
Measles
Key points
• There were 78 suspected cases of measles reported from 47 LGAs in 18 states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date
• National Measles TWG is closely monitoring measles surveillance data and providing feedback to relevant agencies and development partners
• Weekly surveillance and laboratory data harmonisation ongoing
Planned:
• Intensify follow up with states to update and transmit line list
• Continue monthly measles surveillance data review
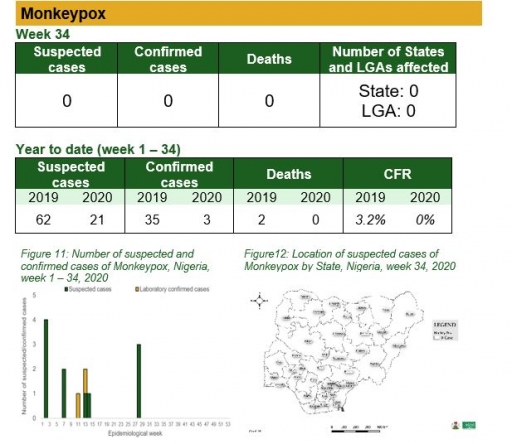
Monkeypox
Key points
• There was no suspected case of Monkeypox reported this week
Actions
To date
• National Monkeypox Technical Working Group (TWG) is monitoring activities in all states
Planned:
• Enhance surveillance for monkeypox in high burden states
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
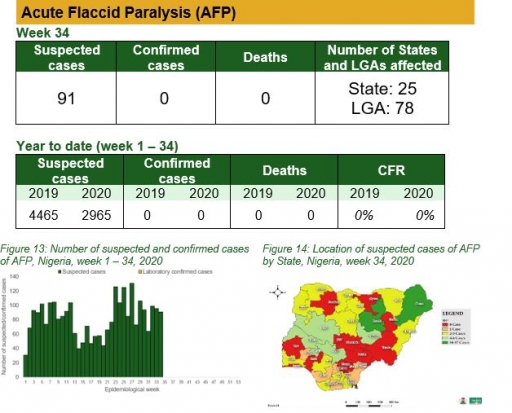
Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP)
Key points
• There were 91 suspected cases of AFP reported from 78 LGAs in 25 states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
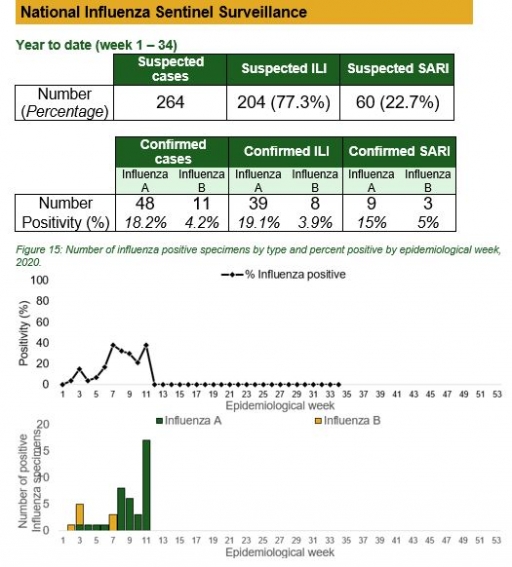
National Influenza Sentinel Surveillance
Key points
• The subtypes A seasonal H3, 2009A/H1N1 and A/not subtyped account for 0 (0.0%), 2 (9.5%) and 19 (90.5%) of the total influenza A positive sample, respectively. The subtypes B VICTORIA, B Not subtyped and B Yamagata account for 0 (0.0%), 8 (100%) and 0 (0.0%) of the total influenza B positive samples, respectively.
• The percentage influenza positive was highest in week 10 with 40%.
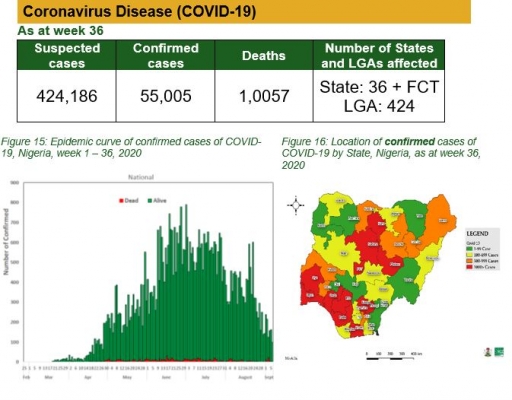
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
Actions
To date:
• National COVID-19 multi-partner Emergency Operations Centre (EOC) continues to coordinate response activities across states
• Currently engaging with states in the South West to commence roll out of digitisation of negative laboratory results
• Developed IPC guidelines on school re-opening
Planned:
• Planning meeting for training of correctional facilities staff on COVID-19 prevention with support of partners is scheduled for September 2020
• Continue to support MDAs to develop plans and guidelines, and advocate for resources to facilitate implementation
• Commence training on the use of the Abbott platform for COVID-19 testing at the Plateau State Specialist Hospital (Plasveric) laboratory, Jos, Plateau State
• Finalise the draft guidelines on intensified surveillance in 'silent LGAs' across the country (LGAs that have not reported a single suspected case)
• Monitoring of state implementation of surveillance activities in the IAP
• Supervision of home-based care services to ensure compliance with IPC standards in Lagos State
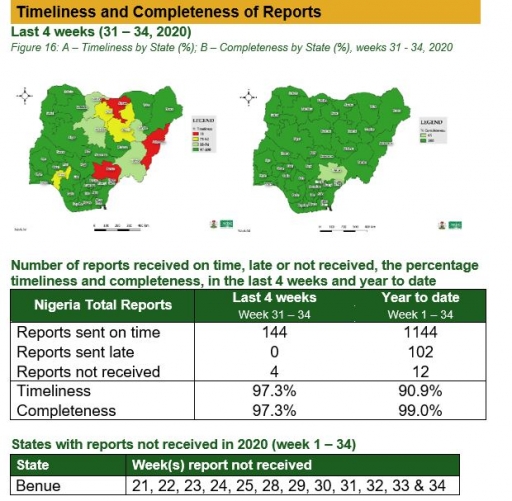
Timeliness and Completeness of Reports
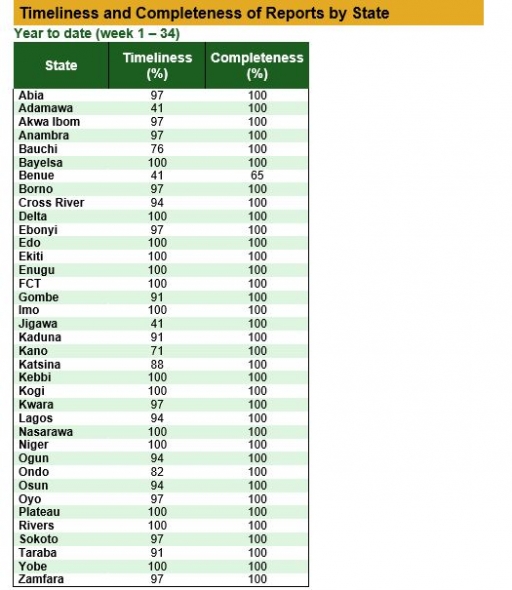
Timeliness and Completeness of Reports by State














 Toll Free Number: 6232
Toll Free Number: 6232 Whatsapp: +234 708 711 0839
Whatsapp: +234 708 711 0839 SMS Number: +234 809 955 5577
SMS Number: +234 809 955 5577 