Editoral
COVID-19: Mitigating Impact Among Vulnerable Population
Posted: 15-07-2020 01:21:30 PM
Research on the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has shown that among populations, some people are at considerably higher risk of having severe complications from the disease. As of the 13th of July 2020, a total of 566,654 deaths have been recorded globally while in Nigeria, a total of 744 deaths have been recorded. Analysis of the case fatality ratio (CFR) in various countries have shown deaths occurring mainly in older adults or persons with underlying health conditions.
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) recently published an updated version of the Advisory for Vulnerable Groups, providing specific guidance on how they can stay protected and reduce the risk of being infected. In line with the context of COVID-19 in Nigeria, people in the following category are considered vulnerable:
1. Persons aged 50 years and older (with or without underlying illnesses)
2. Persons with critical underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, lung disease, liver disease, moderate to severe asthma etc.
3. Other persons who have been assessed as vulnerable, based on clinical assessment
With the gradual reopening of socioeconomic activities nationwide and ongoing community transmission, the risk of being infected is higher particularly where there is inadequate adherence to recommended preventive measures. Below are key excerpts from the advisory, for vulnerable groups, on how to stay safe and protected from COVID-19:
1. Use of non-contact greetings
2. Practice hand hygiene, cough etiquette etc.
3. Avoid non-essential outings, visitors and large gatherings. Always maintain a distance of at least 2 metres of distance between yourself others while in public
4. If possible, consider having your medicines, groceries and essential items delivered to your home by a designated close person who complies with recommended measures including the use of face mask use and hand hygiene
5. If you have to work, discuss and agree your options with your employer to enable you work from home or make changes within the office space to keep you and your colleagues protected
6. If you do share a toilet and bathroom with others, ensure they are cleaned after each use
7. Disinfect frequently touched surfaces e.g., door handles, light switches, TV remotes etc.
8. Where possible, sleep in a different bed and do not share towels, cutlery, drinking cups etc.
9. Keep shared spaces well ventilated and minimise the time spent in shared enclosed spaces, such as kitchens, bathrooms and sitting areas
10. Immediately call your state helpline and a close family member if you develop symptoms of COVID-19 or believe you have been a close contact of a confirmed case.
The NCDC will continue to provide necessary guidelines and public health advisories to ensure Nigerians are protected from COVID-19.
Summary of Incidents
Notes
1. Information for this disease was retrieved from the Technical Working Group and Situation Reports
2. Case Fatality Rate (CFR) for this disease is reported for confirmed cases only
3. Information for this disease was retrieved from IDSR 002 data
4. CFR for this disease is reported for total cases i.e. suspected + confirmed
5. Information for sentinel influenza was retrieved from the laboratory
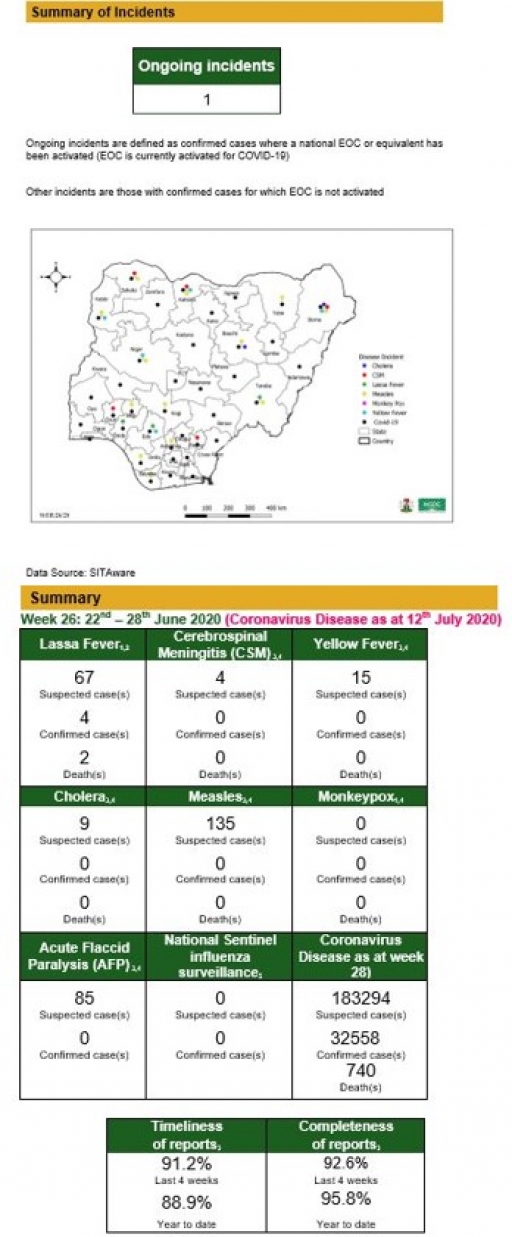
Lassa Fever
Key points
• There were 67 suspected cases, four laboratory confirmed cases and two deaths recorded from nine LGAs in five states
Actions
To date:
• National Lassa fever multi-partner, multi-sectoral Technical Working Group (TWG) continues to coordinate the response activities at all levels
Planned:
• Continue resource mobilisation
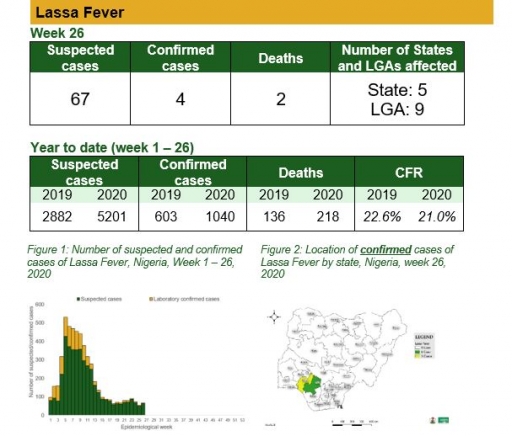
Cerebrospinal Meningitis (CSM)
Key points
There were four suspected cases of Cerebrospinal Meningitis (CSM) reported from four LGAs in four states (Borno – 1, Ebonyi – 1, Katsina – 1 & Sokoto - 1). There was no laboratory confirmed case and no death was recorded
Actions
To date:
• National CSM TWG meets weekly to review reports from states and plan appropriately
• Enhanced surveillance in all states
Planned:
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
• Continue to ensure that states reporting cases send their line lists and collect CSM samples
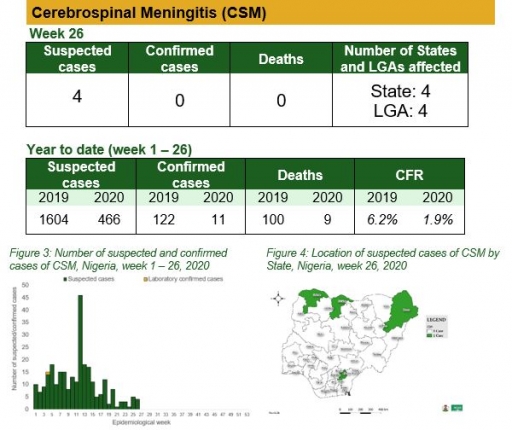
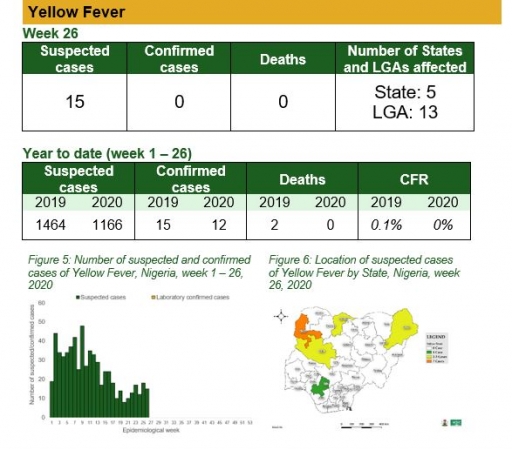
Yellow Fever
Key points
• There were 15 suspected cases of Yellow Fever (YF) reported from 13 LGAs in five states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date:
• National multiagency YF Technical Working Group (TWG) is coordinating response activities
Planned:
• Continue harmonisation of surveillance and laboratory data ongoing
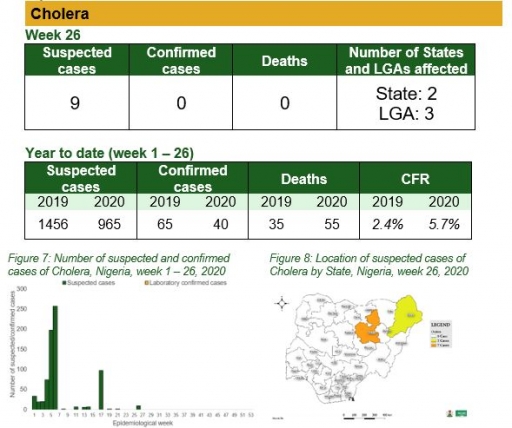
Cholera
Key points
• There were nine suspected cases of Cholera reported from three LGAs in two states (Bauchi – 7 & Borno - 2). None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date
• National Cholera Multi-Sectoral Technical Working Group (TWG) is monitoring all states and supporting affected states
Planned:
• Continue follow up and monitoring of non-reporting states
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
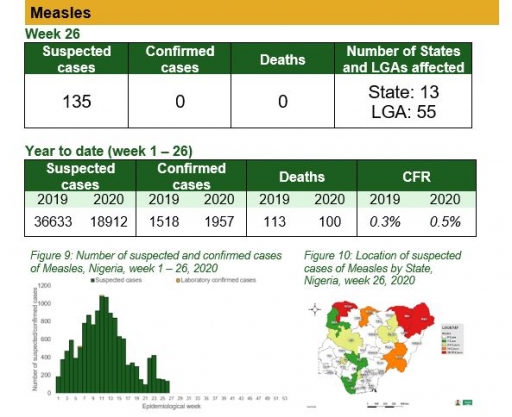
Measles
Key points
• There were 135 suspected cases of measles reported from 55 LGAs in 13 states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
Actions
To date
• National Measles TWG is closely monitoring measles surveillance data and providing feedback to relevant agencies and development partners
• Weekly surveillance and laboratory data harmonisation ongoing
Planned:
• Continue monthly measles surveillance data review
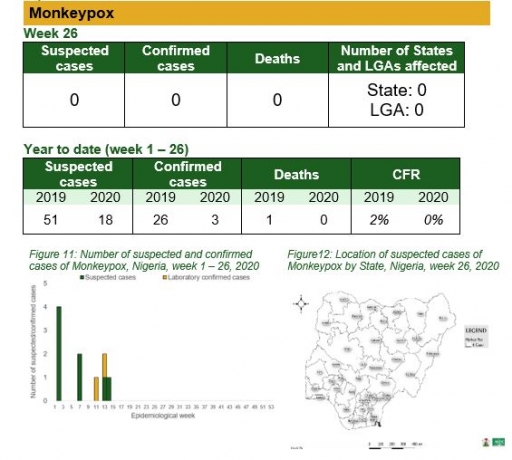
Monkeypox
Key points
• There was no case of monkeypox reported this week
Actions
To date
• National Monkeypox Technical Working Group (TWG) is monitoring activities in all states
Planned:
• Enhance surveillance for monkeypox in high burden states
• Continue harmonisation of the national line list and SORMAS data
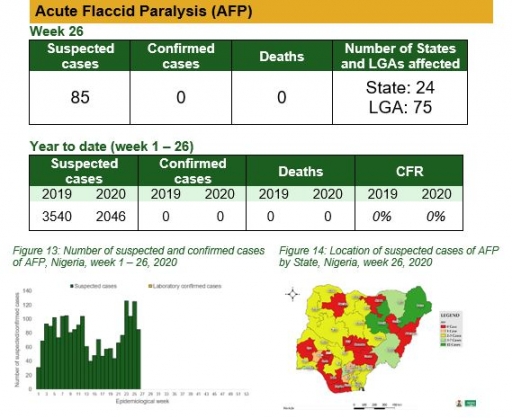
Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP)
Key points
• There were 85 suspected cases of AFP reported from 75 LGAs in 24 states. None was laboratory confirmed and no death was recorded
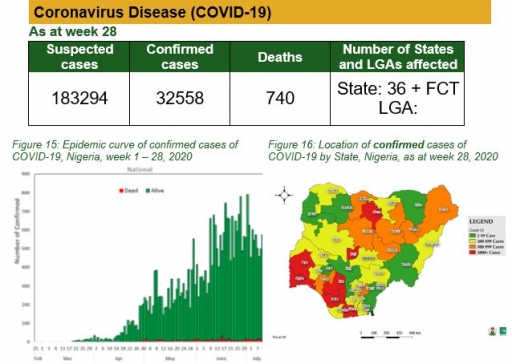
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
Actions
To date:
• National COVID-19 multi-partner Emergency Operations Centre (EOC) continues to coordinate response activities across states
• A total of 41 National Rapid Response Teams have been deployed to support affected states
• Ongoing support to states to expand human resource capacity for contact tracing
• Ongoing capacity building of states IPC trainers through webinars
• Ongoing Collaboration with Logistic Management Coordination Units (LMCUs) in states to collect utilisation data
• Ongoing engagement with stakeholders for buy-in and commitment to the planned school reopening preparedness strategy
• Ongoing monitoring of stock status of commodities deployed to laboratories and treatment centres to forestall stock-out of critical commodities
Planned:
• Develop a checklist for assessing capacity and utilisation of commodities in state-owned warehouses
• Develop data collection tools for qualitative studies
• Activate testing laboratories in Borno, Kaduna, Nasarawa and Niger
• Finalise protocol for expansion of influenza sentinel sites and include COVID-19 testing
• Commence implementation of Events-Based Surveillance (EBS) in six (6)states
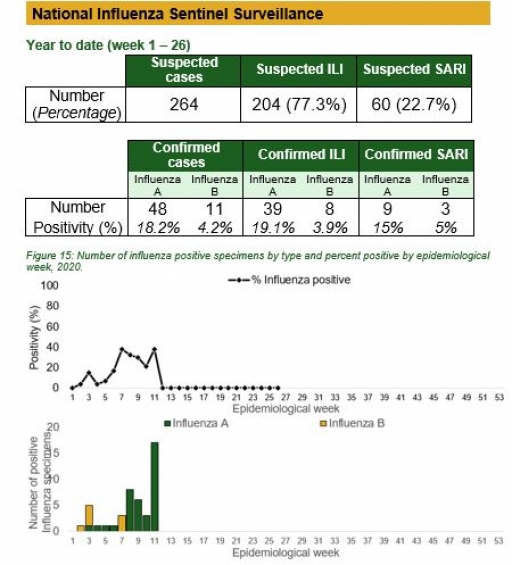
National Influenza Sentinel Surveillance
Key points
• The subtypes A seasonal H3, 2009A/H1N1 and A/not subtyped account for 0 (0.0%), 2 (9.5%) and 19 (90.5%) of the total influenza A positive sample respectively. The subtypes B VICTORIA, B Not subtyped and B Yamagata account for 0 (0.0%), 8 (100%) and 0 (0.0%) of the total influenza B positive samples respectively.
• The percentage influenza positive was highest in week 10 with 40%.
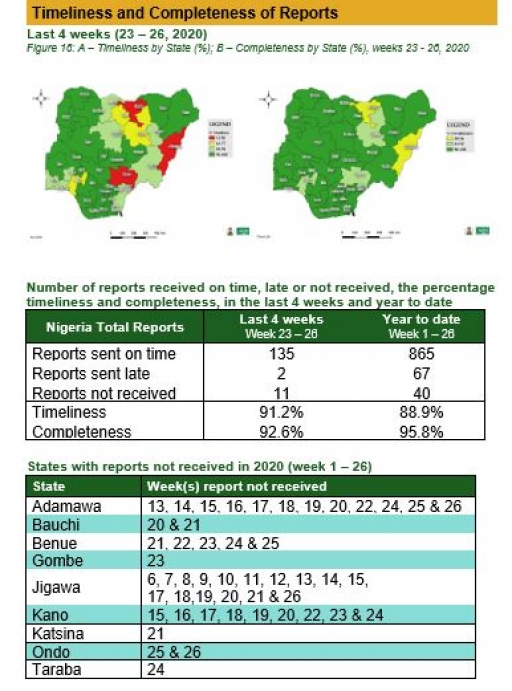
Timeliness and Completeness of Reports
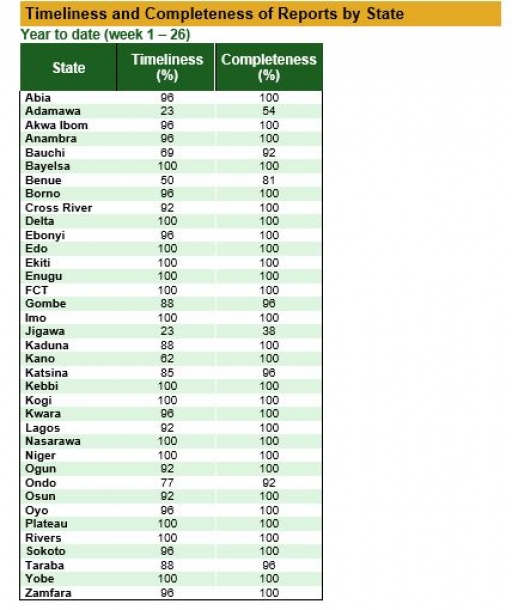
Timeliness and Completeness of Reports by State













 Toll Free Number: 6232
Toll Free Number: 6232 Whatsapp: +234 708 711 0839
Whatsapp: +234 708 711 0839 SMS Number: +234 809 955 5577
SMS Number: +234 809 955 5577 